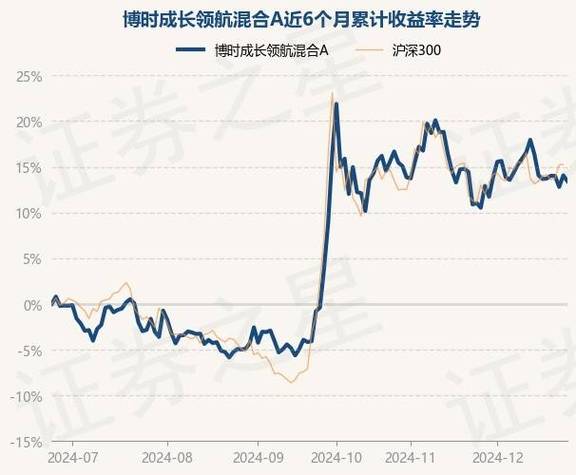
Understanding Your eth0 Network Interface
As a user, it’s crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of your eth0 network interface. This guide will delve into the details of eth0, covering its configuration, troubleshooting, and management aspects.
What is eth0?
eth0 is a common naming convention for the first Ethernet interface in Linux systems. It’s a standard interface used for connecting to local networks and the internet. The ‘eth’ prefix stands for Ethernet, and the number (in this case, 0) indicates the interface’s position in the system.
Checking eth0 Status
To check the status of your eth0 interface, you can use the following command:
ifconfig eth0
This command will display information such as the IP address, subnet mask, and network traffic statistics for eth0.
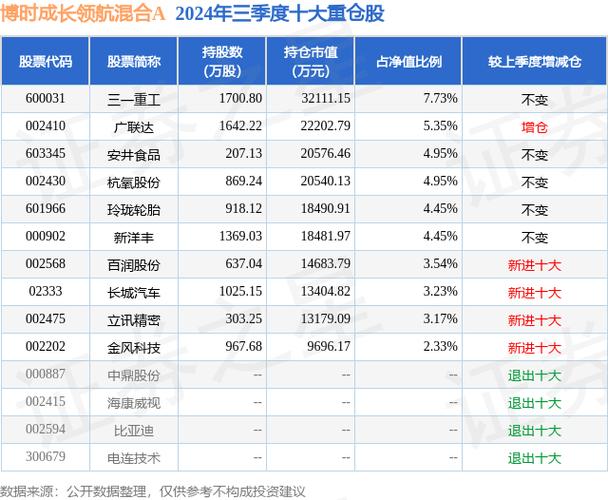
Configuring eth0
Configuring eth0 involves setting up the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. You can do this by editing the network configuration file located at /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| BOOTPROTO | Protocol used to boot the interface (e.g., static, dhcp) |
| ONBOOT | Whether the interface should be activated on boot (yes/no) |
| IPADDR | IP address assigned to the interface |
| NETMASK | Subnet mask for the interface |
| GATEWAY | Default gateway for the interface |
| DNS1 | Primary DNS server |
| DNS2 | Secondary DNS server |
After making changes to the configuration file, save and exit. To apply the changes, restart the network service using the following command:
service network restart
Troubleshooting eth0
If you encounter issues with eth0, here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Check if the interface is up and running using the
ifconfig eth0command. - Ensure that the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway are correctly configured.
- Check for any errors in the
/var/log/messagesfile. - Restart the network service using the
service network restartcommand.
Updating eth0 Driver
Occasionally, you may need to update the driver for your eth0 interface. To do this, follow these steps:
- Identify the current driver using the
lsmod | grep eth0command. - Download the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website.
- Unpack the driver and navigate to the extracted directory.
- Install the driver using the following command:
- sudo make install
- Load the driver using the
modprobe eth0command. - Restart the network service using the
service network restartcommand.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing your eth0 network interface is essential for maintaining a stable and efficient network connection. By following this guide, you should now have a better grasp of eth0’s configuration, troubleshooting, and management.
