Eth Definition for Chemistry: A Comprehensive Overview
Eth, a term that might sound simple at first glance, holds a significant place in the realm of chemistry. Often used in organic synthesis and as a solvent, eth is a compound that has garnered attention for its unique properties and applications. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the definition of eth, its structure, properties, uses, and much more.
What is Eth?
Eth, also known as ethane, is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C2H6. It is a colorless gas at room temperature and pressure, with a boiling point of -88.6掳C and a melting point of -182.8掳C. Ethane is the simplest alkane, which is a class of hydrocarbons that consist of single bonds between carbon atoms.
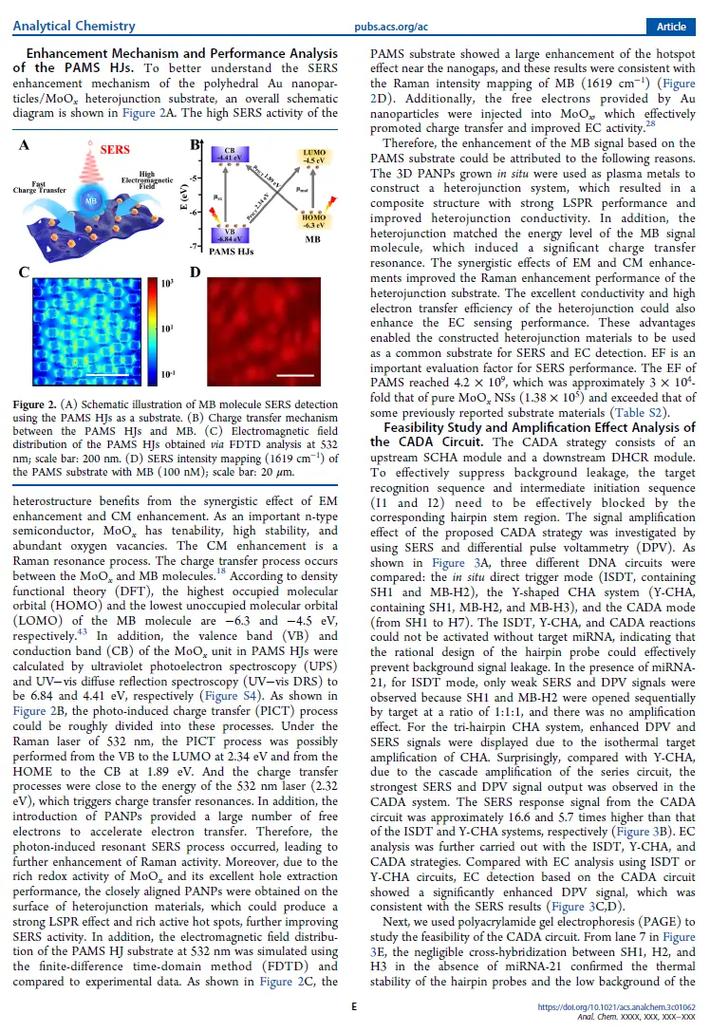
Structure of Eth
The molecular structure of ethane consists of two carbon atoms bonded together by a single covalent bond, with each carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms. This structure gives ethane its linear shape, making it a straight-chain alkane. The carbon-carbon bond length in ethane is approximately 1.54 脜ngstr枚ms, and the carbon-hydrogen bond length is approximately 1.09 脜ngstr枚ms.
Properties of Eth
Ethane is a non-polar molecule, which means it does not have a net electrical charge. This property makes it highly soluble in non-polar solvents, such as hexane and benzene. Ethane is also flammable, with a lower flammability limit of 3.3% and an upper flammability limit of 37%. It is important to handle ethane with caution, as it can pose a fire hazard.
Another notable property of ethane is its low density, which is approximately 0.71 g/L at room temperature and pressure. This low density allows ethane to be easily separated from other substances through distillation. Ethane is also a greenhouse gas, contributing to the Earth’s atmosphere and climate change.
Uses of Eth
Ethane is a versatile compound with various applications in the chemical industry. Some of the most common uses of ethane include:
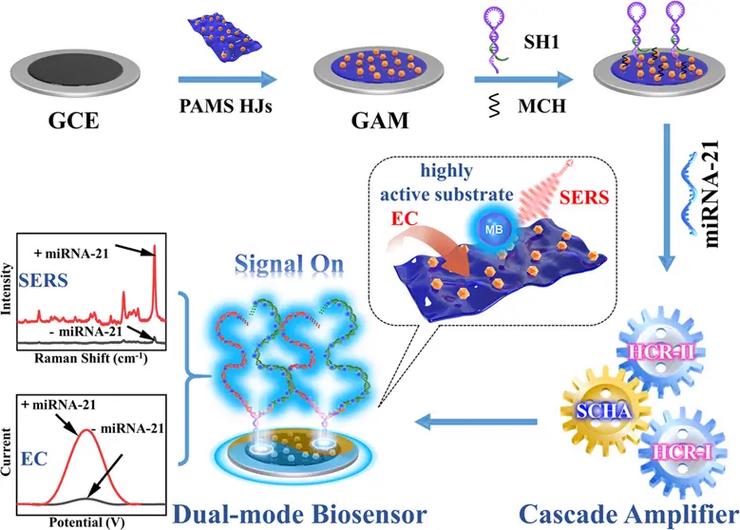
-
As a raw material for the production of ethylene, a key intermediate in the manufacturing of plastics, synthetic rubber, and other chemicals.
-
As a solvent in the extraction of oils and fats from plants and animals.
-
As a fuel in the production of hydrogen and as a component in fuel blends.
-
As a refrigerant in the food and beverage industry.
Environmental Impact
While ethane has numerous applications, it is important to consider its environmental impact. Ethane is a greenhouse gas, and its release into the atmosphere contributes to climate change. Additionally, the extraction and processing of ethane can lead to air and water pollution, as well as the release of other harmful substances.
Efforts are being made to reduce the environmental impact of ethane production and use. This includes the development of more efficient extraction methods, the use of cleaner technologies, and the implementation of stricter regulations to minimize emissions.
Conclusion
Eth, or ethane, is a fundamental compound in the field of chemistry, with a wide range of applications and properties. Understanding its definition, structure, properties, uses, and environmental impact is crucial for anyone interested in the field of chemistry. As the demand for ethane continues to grow, it is essential to address its environmental challenges and work towards a more sustainable future.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | -88.6掳C |
| Melting Point | -182.8掳C |
| Carbon-Carbon Bond Length | 1.54 脜ngstr枚ms |
| Carbon-Hydrogen Bond Length | 1.09 脜ngstr枚ms |
| Flammability Limit | 3.3% – 37% |
